Node.js Web API Boilerplate
02 December 2020
This is a simple Node.js/Express web api with implenmentation of AWS CI/CD, Docker alternative.
In this boilerplate, it deploys a high-availability Node.js web app using AWS Elastic Container Service and MongoDB. The sample app uses Node.js, Express, and a NoSQL database. Using Elastic Container Service, you can simply upload your local images and Elastic Container Service automatically handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling to application health monitoring. Elastic Container Service automatically scales your application up and down based on your application's specific need using easily adjustable Auto Scaling settings.
You can find the github link here
There are two different ways to run this demo, please follow the guide.
Option 1: Local
Make sure you have Mongo and Node installed on your machine.
Setup
Option 2: Docker
Make sure you have docker and docker-compose installed on you machine.
Setup
Cloud && CI/CD Deployment
MongoDB in the docker is to create a simple database without setting up the environment. In this way, initial setup is more efficient and easier to configure. However, it is less applicable deploying the DB to cloud with Docker Compose, not only because the risk or losing data, but also DB instability for multiple service deployment at the same time. In this scenario, MongoDB Atlas will be used as a stable database, you can create your own online.
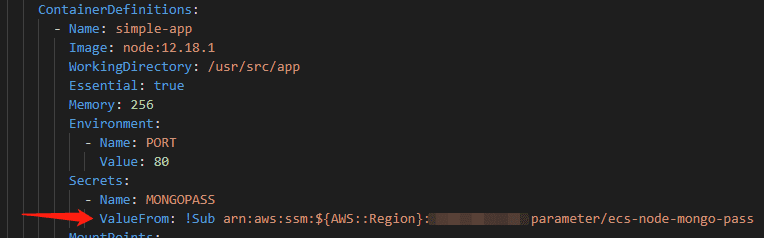
Step One: Create Required AWS Services
I will use Cloudformation to deploy the infrastructure. You can check the templates in the repo. Please upload the templates into S3 bucket as it is a required step to create nested stack. The main template called ecs-continuous-deployment.yaml will generate nested resource stack, including VPC, CodePipeline, Load Balancers, ECS and its service/definition. You can check the flows in the diagram below:
Step Two: Make changes in local and push to github
To identify whether the service has been deployed successfully.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Privacy policy